There have been many researches of robot hands in robot fields and they have been considered one of the most complicated area. There are many reasons why researches of robotic hand are difficult, and these are from complicated structures and functions of hands. There are many types of robotic hands in robotics area, but they can be classified to major two categories. The one is a robotic hand for an operation in industrial area and the other is an experimental hand like human hand. The most of robotic hands in industrial area are 1
D.O.F or 2 D.O.F gripers and they are designed for precise, repetitive operations. In the other area, human like robotic hands, main concerns are how the shape of robotic hands resembles human hands and how the robotic hands can operate like human hands. Most human like robotic hands have 3 ~ 5 fingers like human hands and their shape, size and functions are designed based on human hand. For a long time, major area in researches of robotic hand has been an industrial area, but the importance of human like robotic hands are getting more and more increasing, because the needs of robots will be changed from industrial fields to human friendly environment such as home, office, hospital, school and so on. In brief, the mainstream of robotics will be changed from industrial robots to service robots. One of the important factors for service robots in human friendly environment is their appearance. In general, most of humans are feeling friendly and comfortably to similar appearance like them, so the appearance of service robots should resemble human and their hands should imitate human hands, too. For this reason, there have been many researches for human like robotic hands.
Haruhisa Kawasaki developed Gifu hand 2 which has 5 independent fingers. It has 16 D.O.F and 20 joints, so it is one of the most complicated hands. It can operate all joint of each fingers and with attached tactile sensors, delicate grip can be operated. However, its size is big to install to the human size robot (Haruhisa Kawasaki. et al., 2002). F. Lotti used spring joint and tendon to make UBH 3. It has 5 fingers and human like skin and like Gifu hand, each finger has independent joint. The characteristics of this hand is using a spring to its joint and this make its structure simple, but this hand uses too many motors and they are located in other place, so this hand is not good to humanoid robot (F. Lotti. et al., 2005). Kenji KANEKO developed human size multi fingered hand. It has 13 D.O.F complicated fingers and all devices are located in hand but it has 4 fingers and the back of the hand is too big like glove. In this reason, the shape of this hand is a little bit different to human hand, so it can be used to humanoid robot not android robot (Kenji KANEKO. et al., 2007). The HONDA ASIMO is the most well-known humanoid robot in the world and its hand shape is like human. Its appearance and size is like human and all devices are included in hand but it has only 1 D.O.F, so it is impossible to express variable gestures (K. hirai. et al., 1998) (H. Hirose. et al., 2001). N.Dechev used spring, links and ball nut joint to make multi fingered prosthetic hand. This hand can passive adaptive grasp by using only one actuator and it has human like shape, 5 fingers but it can’t express variable motions because there is only one active joint. This hand shows possibility that prosthetic hands can be applied to human like robot (N. Dechev. et al., 2000). Many of exist hands used motors as actuators but Feifei Zhao used pneumatic type actuators. This hand was made of rubber tube, so there are no links or wires and the structure is so simple. However, this hand can’t make gesture of human finger and its shape is different to human hand (Feifei Zhao. et al., 2006).
The many existing researches of human like hands can be applied to humanoid robots but not matched to android robots. An android robot is one of humanoid robots but its appearance is more similar to human appearance than appearance of humanoid robot. When the android robot is designed, uncanny-vally must be concerned, in particular (Shimada M. et al., 2009). In this reason, the hand of an android required the nearest appearance to human hand than existing variable human like hands and the design is more difficult than one of humanoid hand. There are three required factors to the design of an android robot hands. Firstly, the size is very important, because it must be matched to whole body in proportion. It can be hard to make small size hand due to its complexity, but if the proportion is contrary to human body, it can look ugly. Secondly, even if the size of hand is satisfied, shape must be concerned. Most of humanoid robot hands satisfy the size policy, but the shape is not curved surface like human hand. Mechanical parts are generally angulate, so the space which can be used is narrow and this makes the design of an android robot hand hard. Thirdly, android robot hands need an artificial skin. The artificial skin is major difference between humanoid robot hands and android robot hands. The artificial skins which is used to android robot hands need human like touch, color and flexibility for driving.
In this research, an android robot hand for an android robot EveR 3 is presented. The EveR 3 is an android robot for stage performances as an actress, so the hand of EveR 3 was made for variable gestures as acting not grasping. This hand has five fingers with 5 D.O.F and artificial skin. DC motors and screw-nut are used as actuators and the hand is driven by links. The shape is based on 3D model which was made by scanning data from real human. The artificial skin was made by silicon complex and its shape was also based on 3D model, so its appearance is very similar to human hand.
Design policies
Applied android robot
The presented android robot hand is made for an android robot EveR 3. EveR 3 is the latest model of EveR 1 which was the first android robot in Korea. It was designed for stage performances as an actress. Because this android robot was designed as an actress, it has an elegant appearance and delicate body which can express human like motions. To make human like motions, it has 41 D.O.F (9 D.O.F in face, 22 D.O.F in body, 10 D.O.F in both hands) and its height is 165cm, weight is 55kg. It can move on the stage by two wheeled mobile lower body and was controlled by wireless LAN. Fig.1 shows an android robot EveR 3 with skin, dress and mechanical drawing. Why this robot was made as a woman is to hide the mobile lower body. As an actress, moving on the stage is necessity, but its appearance is different to humans one, so we can hide this parts with long skirt and to wear a skirt, the woman robot is chosen not a man. There is already an android robot can walk, but it is not enough to fast, stable moving (Shin’ichiro Nakaoka. et al., 2009) (Kenji KANEKO. et al.,2009). To make a woman android robot is more difficult than a man android robot, because it has more curved body, narrow space and especially it is more sensitive in appearance. This android robot EveR 3 is based on Korean young woman. To play emotional acting, it has face which has 9 D.O.F and an artificial skin to make expressions. The full body was made by 3D data which is from real human scanning data and this data is also used to make hand, skin. The hand is designed by using this data, so the size and shape are decided from this reference. The artificial skin was also made by this data but little bit different, because the skin design needs making mold. To make mold for an artificial skin, RP (Rapid prototype) mock up was made from 3D data and the mold was made by using mock up. Silicon complex is used as an artificial skin. There are many materials which are reviewed for an artificial skin, but why silicon complex is selected is its characteristics are most like to human skin. The appearance is the most important factor to android robots, so these are design policies for hands.

Fig. 1. The android robot EveR 3 and its mechanical drawing.
Design policies
The goal of this design is to make a human like hand as possible. To achieve this goal, the design policies are established and those are about size, shape and skin. The priority of these policies focused on appearance but not performance.
Size
The size of the hand is based on an android robot which was already mentioned, EveR 3. The model of an android robot EveR 3 is Korean young woman whose height is 165cm and weight is 50kg. When humanoid robots which use real human as model are designed, they use only size like height, length of the limb etc. in general. However, android robots need more strict observation of size not only height, length of joint but also circumference of joint, each part. To make exact reference of model, the original model was scanned by 3D scanner and the scanned data was handled by 3D MAX. From this process, the data which can be used CAD program (Solid works) was earned. This data contained all information of size of original model and this can measure exactly by CAD. The size of hand from original model can be measured exactly, too. The required size data which is needed to realize same size of original model is length of each finger, length of each joint of finger, circumference of each finger, thickness of palm and length of palm. Of course, it is hard to realize exact size of each factor of original model, but this process can help to make a robot hand which is the nearest to human hand than any other existing hands. Fig. 2 shows the real size of robotic hand especially mechanical structure and comparison with real human hand whose is the designer of this hand (168cm, Korean man). Even if this man’s hand is small, the robotic hand is smaller than his one. Table.1 shows parameters of main factor which are considered to design.

Fig. 2. Mechanical part of robotic hand and comparison with real human hand.
| Total length | 168 mm (from fingertip to wrist joint) |
| Width | 80 mm (when thumb finger is bended) |
| Thickness (Palm) | 27 mm |
| Weight | 450 g |
| Index finger | 37/23/ 18 mm (1st, 2nd, 3rd joint) |
| Middle finger | 40/28/18 mm (1st, 2nd, 3rd joint) |
| Ring finger | 36/25/18 mm (1st, 2nd, 3rd joint) |
| Little finger | 26/18/15 mm (1st, 2nd, 3rd joint) |
| Thumb finger | 32/18 mm (1st, 2nd, 3rd joint) |
Table 1. The pamameters of developed android hand.
Shape
The consideration of shape of an android robot hand is as important as one of its size. There are many humanoid robot hands whose size satisfy human like size, because humanoid robots are designed as real human size. However, most of their designs are not like real human hand especially shape. Even if humanoid robots have similar appearance to human, its design is based on robot basically, so shape of human is curved but one of humanoid robots is angulate (AKACHI K. et al., 2005) (Ill-Woo Park. et al., 2005) (Jun-Ho Oh. et al.,2006). The android robot hand should have curved design and it make hard to design, because most of mechanical parts are angulate, so the space which can be used is very narrow. To design human like curved shape, 3D scanned hand data which was already mentioned was used. There is consideration to use that data. The shape of this data is full straightened, so it is hard to know the shape when the finger bended. Some processing was applied to original data to make bended shape by 3D graphics program (Maya). Fig. 3 shows variable shape of finger to check. From these processes, the nearest reference 3D data to real human hand can be obtained.
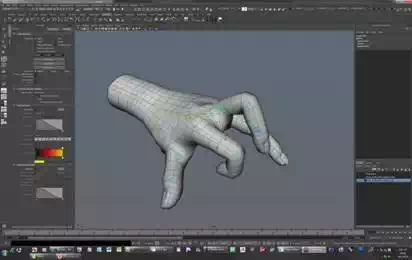
Fig. 3. The handled 3D data to check shape by graphics program.
Skin
The skin is the most important factor to make human like hand, because skin is the part which is shown intuitively. There are some considerations for an artificial skin. These are texture, color and details like wrinkle, so it needs not only technology but also arts. The silicon composite was selected as an artificial skin, because it is the closest material to human skin than any other materials and it is easy to handle. The artificial skin also used 3D data as a reference, but there are more steps to use. To make a silicon complex skin, the mold is needed, because the process of making silicon complex is like one of making plasters. The 3D data was used to make mock up model. To make exactly same model to original model, RP (Rapid prototype) was used to make mock up model. After making mock up, mold was made by using this mock up model, and a silicon complex skin can be made. The artificial skin which is made by silicon complex is very similar to human skin, but to raise the similarity, make up was taken in final step. Though the mechanical part was made by consideration of shape, there are gaps between parts and skin. This gaps can make wrinkles when the finger bended. To solve this problem, art clay was attached to gaps between mechanical parts and skin. Fig. 4 shows a silicon composite artificial skin for hand.
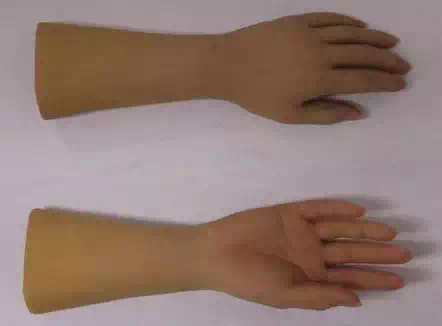
Fig. 4. A silicon composite artificial skin for an android robot hand.
Hardware design
Finger design
The finger design is the most important part in this android robot hand. The presented hand has 5 fingers like human hand and total 5 D.O.F with 1 D.O.F each finger. Actually, human finger has 3 D.O.F at proximal joint, middle joint and distal joint to bend or stretch and 1
D.O.F to spread, so there are 4 D.O.F in each finger basically. In case of thumb finger, there is no middle joint, so it has 3 D.O.F (proximal, distal and 1 D.O.F for abduction and adduction). There are at least 25 D.O.F in real hand, so it is very hard to realize by robotic hands, because there are not enough spaces to install actuators in hand. For this reason, most of humanoid or android hands have smaller number of D.O.F than one of human. Of course, there are some hands which have many D.O.F like one of human, but their size are bigger than human hands (H. Liu. et al., 2008) or they have other large spaces which have a lot of actuators instead (Yuichi Kurita. et al., 2009). For these reasons, the hands for humanoid robots or android robots should have less D.O.F than one of human hand. In this research, the 5 D.O.F hand is designed to express fundamental motion of human hand like straightening – bending of each finger. The best feature of this hand is that the each finger was made as a modular structure independently. Most of robotic hands have their actuators like motors in palm or forearm and their finger is connected to palm, but the finger of this hand has an actuator (DC motor), sensor and gears as its own components. The combination of these components becomes independent finger module. Why this finger was designed as a module is for easy maintenance.
The android robot EveR 3 which this hand is applied to was designed for stage performance especially commercial performances not just using in the laboratory for researches, so reliability and maintenance is one of the most important factors. The modular structure can give fast and easy maintenance of hardware. For example, when the middle finger breaks down, replacing of the middle finger module is the only maintenance of all. It is fast, easy and low cost. Fig. 5 shows the disassembled hand by each module.
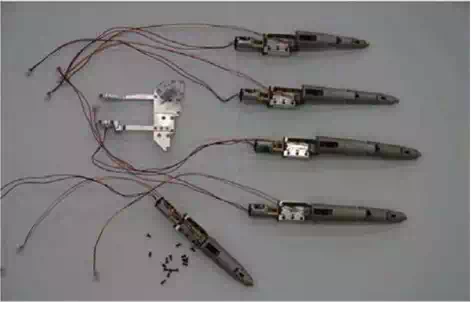
Fig. 5. The disassembled hand by each module (fingers and palm).
The organization of a finger module consists of a geared DC motor as an actuator, a screw- nut, a linear potentiometer and joint links. The joint links are composed of three phalanges as a proximal joint, middle and a distal like human finger. In case of a thumb finger, it is little different to other fingers. There are only a proximal and a distal phalange. These phalanges are frame of finger and these joints are connected inner links and the inner links make subordination of driving of three joints. Fig. 6 shows the composition of a finger module.
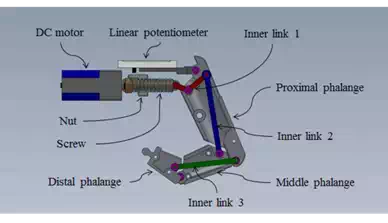
Fig. 6. The composition of a finger module.
The power of the used DC motor is 6mNm and it uses 5V (GM-12F, Motor Bank). The dimension of motor is 36x10x12mm (including gear head) and its weight is 10g. The power of motor is not enough to drive the finger with skin, a gear head whose ratio is 1/50 was attached to the motor. The screw-nut is used to drive links of finger for saving spaces. If the motor is placed to rotation of links horizontally, it is hard to arrange the motors, because all joints of proximal phalanges are placed in same axis. The advantage of this type to arrange motors is easy to design and disadvantage is using of space ineffectively. To place motor vertically to rotational axis of links, worm gear, bevel gear or screw-nut can be considered which connect motor to joint. Why the screw-nut is selected is that it is easy to make small size and a linear potentiometer can be attached to nut. The nut is connected to a linear potentiometer and an inner link 1. The linear potentiometer (RDC1047, ALPS) is used to feedback control of motor and initialize. The motor is small, so it is hard to attach an encoder to it, so the linear potentiometer is used by calculating of gear ratio and lead of screw-nut, the RPM of motor can be obtained. The linear potentiometer uses 5V and its linearity is +/- 5%. The most of parts are made by aluminum (6061alloy) for light weight, a screw-nut is made by brass for low friction and inner links are made by steel (sus304).
Mechanism of motion
The motion of the finger is occurred by rotation of inner link 1 and the one of left links are subordinated by kinematic relation. Fig. 7 describes the motion of each links when the finger bended and straightened. The motion of finger can be described by following. The proximal phalange is connected to housing of actuating parts and middle phalange, distal phalange are connected in serial order. Three inner links are connected among three phalanges and these inner links make subordinate relation of each phalange. The inner link 1 is connected to nut and its center of rotation is located under of proximal phalange and their centers of rotations are different, so when the inner link 1 is pulled by nut; the proximal phalange rotates by difference of their center of rotation. The shape of inner link 1 is like a boomerang and each tail is connected to nut and inner link 2, so when the inner link 1 is pulled, it starts rotate and it pulls inner link 2. The mechanism of rotation of middle phalange is same to one of proximal phalange. The inner link 2 is connected to middle phalange and the point is different to the center of rotation of the middle phalange, so when the inner link 2 is pulled by inner link 1, the middle phalange rotates. The inner link 3 is connected to proximal phalange and distal phalange. The connected point of inner link 3 in proximal phalange is different to the center of rotation of the middle phalange and the connected point in distal phalange is different to the center of rotation of distal phalange. When the inner link 3 is pulled by rotation of the middle phalange, the distal phalange rotates as same to the middle phalange.
The angle of rotation of each joint is decided by the length and center of rotation of each inner links. The length of proximal phalange, middle phalange and distal phalange is fixed value which is based on the original human model, so the values of inner links (length, position of center of rotation) are design factors in this hand. This robotic hand was made to gesture but not grasp. The gesture which is purposed is natural fist, so the design factors of the inner links are decided when fully bended shape of hand becomes fist. The angles of proximal joint, middle joint and distal joint are 60 degree, 90degree and 45 degree when the shape of hand is fist. The structure of fingers is same except the thumb finger but the sizes are different. In case of human hand, the middle finger is the longest, the index finger and ring finger are similar, and little finger is the smallest size, so this hand wad followed that order.
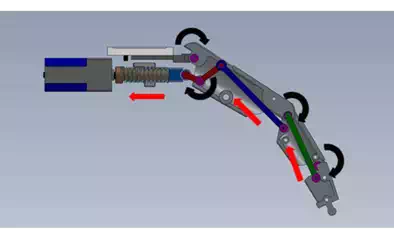
Fig. 7. The mechanism of bending.
Palm and wrist design
The design of palm is simple as compared with the one of finger. The presented hand is just combination of finger modules, so the palm part is the connecter of finger modules. Even if the role is simple, there are some considerations in palm design, because it can decide the shape of hand by arrangement of finger modules. The most of robot fingers are arranged in same axis in front, top view but in case of human, they are different. The design of palm considered this difference, so the height and distance of each fingers is adjusted by arrangement of attached points. Fig. 8 shows arrangement of finger modules. The one more consideration of palm design is the attachment of thumb finger. The human thumb finger has 3 D.O.F especially including abduction-adduction and some of humanoid robot has same D.O.F. In case of robot hand which is designed for grasping, the D.O.F for abduction- adduction motion is very important, but in this research, there is only 1 D.O.F by out of space. Because the only 1 D.O.F is for bending, the attachment to palm is important to decide the shape of hand. The attachment position is considered natural shape of hand when the hand is fully straightened and fist. The attachment angle is decided 81 degree in top view and 15 degree in front views. This arrangement is shown in Fig. 8. The angle and position are decided by one part and the shape can be changed easily by replacement of this part, thumb connecter. The palm part consists of a palm connecter which connects 4 finger modules, thumb connecter and wrist connecter, so it is very simple and it is easy to change the shape.
The wrist design is based on 3D model like hand design. The human wrist has 2 D.O.F but the wrist of this robot has 1 D.O.F by out of space. The wrist design is included to forearm design and this forearm has wrist joint, forearm yaw joint and controllers for hand and forearm, so there are space problems. To solve this problems, smallest harmonic drive (CSF-5-100-2XH, Harmonic drive), BLBC motors (RE20Flat 5W, Maxon) and self-developed controller was used for getting over narrow space problem. The controller for hand used DSP and it has 6 analog input ports for sensors (Linear potentiometer) and it can control 6 DC motors. Though this hand has 5 D.O.F, this controller has 6 ports for abduction- adduction motion of thumb finger in future works. The BLBC controller was also self- developed to satisfy small spaces. It can control 2 BLDC motors and there are 4 ports for encoders, proximity sensors and it used DSP, too. The proximity sensor (GL-6H, Sunx) was used for initializing. From these efforts, slim size wrist design which can match to reference model can be made. Fig. 9 shows the wrist design and controllers.
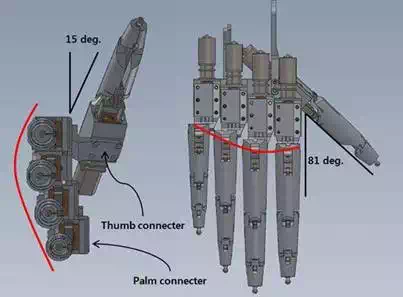
Fig. 8. The shape of palm, thumb joint and attachment position.
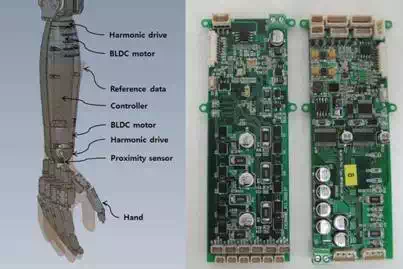
Fig. 9. The wrist design and controllers (hand controller, forearm controller).
Skin design
The skin part, especially an artificial skin, is very important factor of hand for an android robot, because it is the only shown part optically in outside. The skin design is basically similar to one of hand, but there are more steps than hand design. There are three steps to make skin part.
These are mock up, mold and material making. Firstly, the mock up is made by original 3D model. This mock up is used to make mold for skin, so it is needed to be like original model as possible. To realize original model exactly, the mold was made by RP (Rapid prototype) and the exact same model to original can be made. Secondly, the mold was used to cast skin and this is made by mock up. This process is similar to make a plaster caster. The mold was made by silicon, but this is not tough to make skin several times. The CNC based metal mold was replaced to the silicon mold and this mold was tough to use several times, but it was expensive to make. Thirdly, the artificial skin is made by mock-up and mold. There are some materials as an artificial skin like urethane, latex, rubber and silicon. The silicon complex was selected the material of artificial skin, because it has the closet texture to human skin and it is easy to handle. In addition, the characteristic of silicon can be changed easily by the mixture ratio of an emulsion. This mixture ratio between silicon and an emulsion decides the durableness of the skin. It is very important the durableness of material to make an artificial skin, because if the durableness of the skin is hard, it can be stiff resistance to move but soft, it tears easily. Through many times of experiments, the optimal mixture ratio between silicon and an emulsion can be obtained. The pigments were used to make human like color and they were made by blending of some colors and added with an emulsion. After completion of skin, the wrinkles are added to skin by make-up to raise reality.
Even if this artificial skin of hand can realize the human hand and mechanical parts are designed by 3D data from human, there are some gaps between skin and mechanical parts. The kind of art clay was used to fill these gaps. The art clay is easy to handle and build shape. From these processes, the artificial skin for robo hand which has the closest shape to human can be produced. Fig. 10 shows the mock-up, mold and the artificial skin.
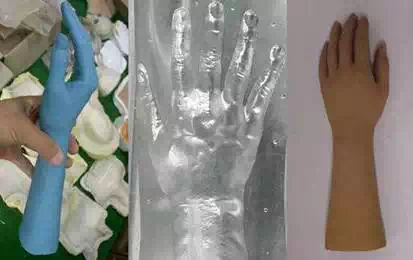
Fig. 10. The mock-up, mold and finished artificial hand skin
Kinematics of finger modules
o
.
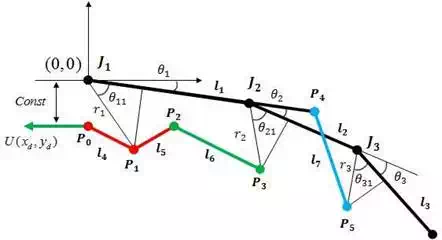
Fig. 11. The simplified image of finger and parameters
| J1 | Proximal joint |
| J2 | Middle joint |
| J3 | Distal joint |
| l1 | Proximal phalange |
| l2 | Middle phalange |
| l3 | Distal phalange |
| l4 | Inner link 1 |
| l5 | Inner link 1 (other limb) |
| l6 | Inner link 2 |
| l7 | Inner link 3 |
| U(xd , yd ) | Distance by screw-nut (input) |
Table 2. Parameters for kinematics


| 3 y 2 y |
l6
(P3x P2 x )
2 (P P )2
(3)
P3 f ( J2 )
The l6 is the designed value and P3 can be known by forward kinematics from J2 . These formulas are also solved by Matlab, because they are too complicated to solve by hand.
The structure of distal joint is simple 4 bar linkage, so the 3 can be solved easier than 1 , 2 . The 3 is known by solving simultaneous equations (4).

| 4 y 3 y |
l7
(P4 x P3x )
2 (P P )2
(4)
P5 f ( J3 )
How to get unknown values is same to get unknown in 2 .
Even if the complicated kinematics was solved, it was not used to operate hand except for
calculating 1 .
Experiment and discussions
This hand was made for gestures like human hand not grasping, so experiments are very simple. From this purpose, the experiments were taken to check how this hand can realize gestures like the one of human similarly and verify the torque of hand is enough or not to move under the resistance of skin. Even if some experiments were taken to know the resistance of skin by pieces of silicon, there are great differences between pieces of skin and hand shaped skin. The exact experiments can be taken by material engineering area, so it was not efficient way to check the resistance of skin, tests to the real model was taken. The performed experiments to gestures are basically to express rock-paper-scissors posture. The 6 postures are performed including rock-paper-scissors and during these postures, how the shapes are natural like the shape of hand of human in same posture was checked. The tearing and wrinkle at the surface, adequateness of torque are also checked. Fig. 12 shows 6 postures with the completed hand. The gear ratio was 1/30 at first, but it is not enough to bend the finger fully, so the gear ratio was changed to 1/50 and it worked well. In addition to change of the gear ratio, the thickness of skin was thinner and this made problem. Because the transmittance becomes high, the inner mechanical part can be shown even if there is make-up to the skin. The mixture ratio among silicon, pigments and an emulsion should be more researched. There are no barometers for a point of similarity between presented hand and human hand, so the evaluation of this hand is subjectively. The esthetic valuation basis should be needed as future works. There are some needs of improvement after experiments. Firstly, the exact measure of the resistance of skin is needed. It is not easy to know the resistance of the real shape, but trial-error ways are not efficient. Secondly, the cost of hand is too expensive. This hand is not just for researches, the cost is one of the most important factors. The small and exquisite parts caused high cost, so the more simple structure and parts should be designed. Thirdly, the 1 D.O.F thumb finger and no spread of fingers are not enough to gesture like human. Even if there are not enough spaces in hand, the spread fingers and abduction-adduction motion of thumb finger should be added to make natural gestures like human.
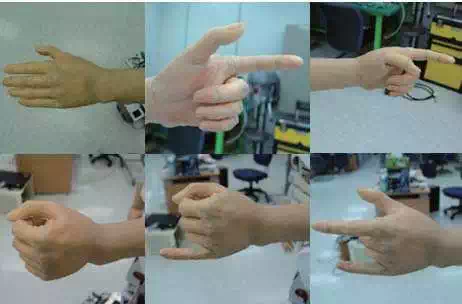
Fig. 12. The 6 postures with completed hand.
Conclusion
In this paper, 5 D.O.F hand for an android robot with an artificial skin was presented. The hand of an android robot required human like appearance because of an android robot is the nearest robot to human. The presented robotic hand has 5 D.O.F fingers and its shape and size are based on Korean young woman. There are three design policies which are size, shape and skin to make this hand and these are for the closest realization of human hand. The finger used D.C motor, screw-nut and liner potentiometer and linkage structure as a power transmission. The characteristic of mechanical design is a modular structure. Each finger module has its own power and sensor independently, so this design can bring easy maintenance by changing modules. The finger module was designed to suit the shape which is based on 3D data from human hand. The hand is just combination of each finger module and palm part. The palm part decides the shape of hand by arrangement of finger modules and it is also designed by 3D data based on human hand. The artificial skin was made of silicon complex which was selected as the nearest material to human skin. To make this silicon complex, mock-up and mold and mixture of materials are needed. After these processes, the closest android hand to real human hand can be produced. This hand is not for grasping but gesture, so experiments are for evaluation how it has similar appearance to human hand and can make variable gestures. In experiments, this hand can express variable postures include rock-paper-scissors and its appearance is similar to human hand. There are some improvements to this hand. The 5 D.O.F is not enough to realize variable gestures of human hand especially spread of fingers and adduction-abduction. In addition, the exact valuation standard of similarity in appearance should be researched. These should be the future works in this research.



Comments are closed